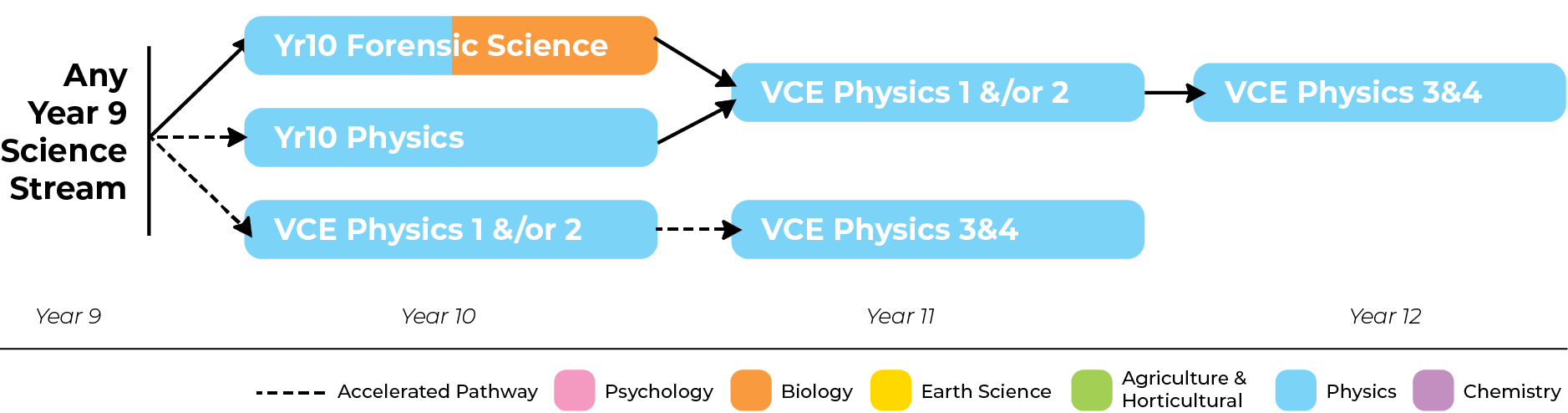
Physics Pathways
Physics Unit 1


Overview
In this unit you will examine some of the fundamental ideas and models used by physicists in an attempt to understand and explain energy. Models used to understand light, thermal energy, radioactivity, nuclear processes and electricity are explored. You apply these physics ideas to contemporary societal issues: communication, climate change and global warming, medical treatment, electrical home safety and Australian energy needs.
Unit Prerequisites
Year 10 Physics or Year 10 Forensics are recommendations.
Areas of Study
- How are light and heat explained?
- How is energy from the nucleus utilised?
- How can electricity be used to transfer energy?
Download > VCE Physics Study Design
Unit Assessment
Assessment tasks for Outcomes 1, 2 and 3 may include a laboratory report, a media response, a problem solving task, experimental analysis, a physics referenced response to a real world issue or a modelling or simulation activity.
Pathways
It is recommended that both Units 1 &/.or 2 be taken as preparation for Units 3 & 4, but Unit 1 is preferred if both cannot be completed. Note that Unit 1 and/or 2 may be completed in Year 10, followed by Unit 3/4 in Year 11. Students undertaking Physics would be expected to be competent in Mathematics as well as in the Physics components of a Science course.
Physics Unit 2

Overview
How does physics help us to understand the world?
In this unit you explore the power of experiments in developing models and theories. You investigate a variety of phenomena by making your own observations and generating questions, which in turn lead to experiments.
In Area of Study 1, you investigate the ways in which forces are involved both in moving objects and in keeping objects stationary and apply these concepts to a chosen case study of motion.
In Area of Study 2, you choose one of eighteen options related to climate science, nuclear energy, flight, structural engineering, biomechanics, medical physics, bioelectricity, optics, photography, music, sports science, electronics, astrophysics, astrobiology, Australian traditional artefacts and techniques, particle physics, cosmology and local physics research. The selection of an option enables students to pursue an area of interest through an investigation and using physics to justify a stance, response or solution to a contemporary societal issue or application related to the option.
A student-adapted or student-designed scientific investigation is undertaken in Area of Study 3. The investigation involves the generation of primary data and draws on the key science skills and key knowledge from Area of Study 1 and/or Area of Study 2.
Unit Prerequisites
Unit 1 Physics is highly recommended.
Areas of Study
- How is motion understood?
- Options: How does physics inform contemporary issues and applications in society?
- How do physicists investigate questions?
Download > VCE Physics Study Design
Unit Assessment
Assessment tasks for Outcomes 1 and 2 may include a laboratory report, a media response, a problem solving task, experimental analysis, a physics referenced response to a real world issue or a modelling or simulation activity. Assessment for Outcome 3 will be a report of a student-led practical investigation using a scientific poster.
Pathways
It is recommended that both Units 1 &/or 2 be taken as preparation for Units 3 & 4, but Unit 1 is preferred if both cannot be completed. Note that Unit 1 and/or 2 may be completed in Year 10, followed by Unit 3/4 in Year 11. Students undertaking Physics would be expected to be competent in Mathematics as well as in the Physics components of a Science course.
Physics Unit 3


Overview
How do fields explain motion and electricity?
In this unit students use Newton’s laws to investigate motion in one and two dimensions. They explore the concept of the field as a model used by physicists to explain observations of motion of objects not in apparent contact. Students compare and contrast three fundamental fields – gravitational, magnetic and electric – and how they relate to one another. They consider the importance of the field to the motion of particles within the field. Students examine the production of electricity and its delivery to homes. They explore fields in relation to the transmission of electricity over large distances and in the design and operation of particle accelerators.
A student-designed practical investigation involving the generation of primary data and including one continuous, independent variable related to fields, motion or light is undertaken either in Unit 3 or Unit 4, or across both Units 3 and 4, and is assessed in Unit 4, Outcome 2. The design, analysis and findings of the investigation are presented in a scientific poster.
Prerequisites
It is recommended that both Units 1 & 2 be taken as preparation for Units 3 & 4. Note that Unit 1 and/or 2 can be taken in Year 10 (Unit 1 is the recommended option if both Unit 1 and 2 cannot be completed), followed by Unit 3 and 4 in Year 11. Students undertaking Physics would be expected to be competent in Mathematics as well as in the Physics components of a Science course.
Areas of Study
- How do physicists explain motion in two dimensions?
- How do things move without contact?
- How are fields used in electricity generation?
Download > VCE Physics Study Design
Unit Assessment
- Unit 3 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 30%
- Unit 4 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 20%
- Unit 3 & 4 examination 50%
Assessment for Outcomes 1, 2 and 3 may include tasks selected from
- application of physics concepts to explain a model, theory, device, design or innovation
- analysis and evaluation of primary and/or secondary data, including data plotting, identified assumptions or data limitations, and conclusion
- problem-solving, applying physics concepts and skills to real-world contexts
- comparison and evaluation of two solutions to a problem, two explanations of a physics phenomenon or concept, or two methods and/or findings from practical activities.
Unit 3 or 4 Practical Investigation: A student-designed or adapted investigation related to light, fields or motion is undertaken in either Unit 3 or Unit 4, or across both Units 3 and 4. The investigation is to relate to knowledge and skills developed across Units 3 and 4 and may be undertaken by the student through laboratory work.
Physics Unit 4

Overview
How have creative ideas and investigation revolutionised thinking
in physics?
A complex interplay exists between theory and experiment in generating models to explain natural phenomena. Ideas that attempt to explain how the Universe works have changed over time, with some experiments and ways of thinking having had significant impact on the understanding of the nature of light, matter and energy. Wave theory, classically used to explain light, has proved limited as quantum physics is utilised to explain particle-like properties of light revealed by experiments. Light and matter, which initially seem to be quite different, on very small scales have been observed as having similar properties. At speeds approaching the speed of light, matter is observed differently from different frames of reference. Matter and energy, once quite distinct, become almost synonymous.
In this unit, students explore some monumental changes in thinking in Physics that have changed the course of how physicists understand and investigate the Universe. They examine the limitations of the wave model in describing light behaviour and use a particle model to better explain some observations of light. Matter, that was once explained using a particle model, is re-imagined using a wave model. Students are challenged to think beyond how they experience the physical world of their everyday lives to thinking from a new perspective, as they imagine the relativistic world of length contraction and time dilation when motion approaches the speed of light. They are invited to wonder about how Einstein’s revolutionary thinking allowed the development of modern-day devices such as the GPS.
A student-designed practical investigation involving the generation of primary data and including one continuous, independent variable related to fields, motion or light is undertaken either in Unit 3 or Unit 4, or across both Units 3 and 4, and is assessed in Unit 4, Outcome 2. The design, analysis and findings of the investigation are presented in a scientific poster format.
Prerequisites
It is recommended that both Units 1 & 2 be taken as preparation for Units 3 & 4. Note that Unit 1 and/or 2 can be taken in Year 10 (Unit 1 is the recommended option if both Unit 1 and 2 cannot be completed), followed by Unit 3 and 4 in Year 11. Students undertaking Physics would be expected to be competent in Mathematics as well as in the Physics components of a Science course.
Areas of Study
- How has understanding about the physical world changed?
- How is scientific inquiry used to investigate fields, motion or light?
Download > VCE Physics Study Design
Unit Assessment
- Unit 3 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 21%
- Unit 4 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 19%
- Unit 3 & 4 examination 60%
Assessment for Outcomes 1 and 2 may include tasks selected from
- application of physics concepts to explain a model, theory, device, design or innovation
- analysis and evaluation of primary and/or secondary data, including data plotting, identified assumptions or data limitations, and conclusions
- problem-solving, applying physics concepts and skills to real-world contexts
- comparison and evaluation of two solutions to a problem, two explanations of a physics phenomenon or concept, or two methods and/or findings from practical activities.
Unit 3 or 4 Practical Investigation: Communication of the design, analysis and findings of a student-designed and student-conducted scientific investigation through a structured scientific poster and logbook entries.

