Physical Education
Units 1+2



Overview
Unit 1 | The Human Body in Motion
In this unit, students explore how the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems work together to produce movement. Students investigate the role and function of the main structures in each system and how they respond to movement. Through participation in practical activities, students explore and analyse the relationships between the body systems and movement, and how these systems interact and respond at various intensities.
Students investigate possible conditions and injuries associated with the musculoskeletal system and recommend and implement strategies to minimise and manage such injuries and conditions. They consider the ethical implications of using permitted and prohibited practices to improve the performance of the body systems, evaluating perceived physiological benefits and describing potential harms.
Areas of Study
- How does the musculoskeletal system work to produce movement?
- What role does the cardiorespiratory system play in movement?
Unit 2 | Physical Activity, Sport, Exercise and Society
This unit develops students’ understanding of physical activity, sport and exercise from a participatory perspective. Students are introduced to types of physical activity and the role that physical activity participation and sedentary behaviour plays in their own health and wellbeing, as well as in other population groups and contexts.
Through a series of practical activities, students experience and explore different types of physical activity promoted within and beyond their community. They gain an appreciation of the movement required for health benefits and the consequences of physical inactivity and sedentary behaviour. Using various methods to assess physical activity and sedentary behaviour, students analyse data to investigate perceived barriers and enablers, and explore opportunities to enhance participation in physical activity. Students explore and apply the social-ecological model to critique a range of individual- and settings-based strategies that are effective in promoting participation in regular physical activity. They create and participate in a personal plan with movement strategies that optimise adherence to physical activity and sedentary behaviour guidelines.
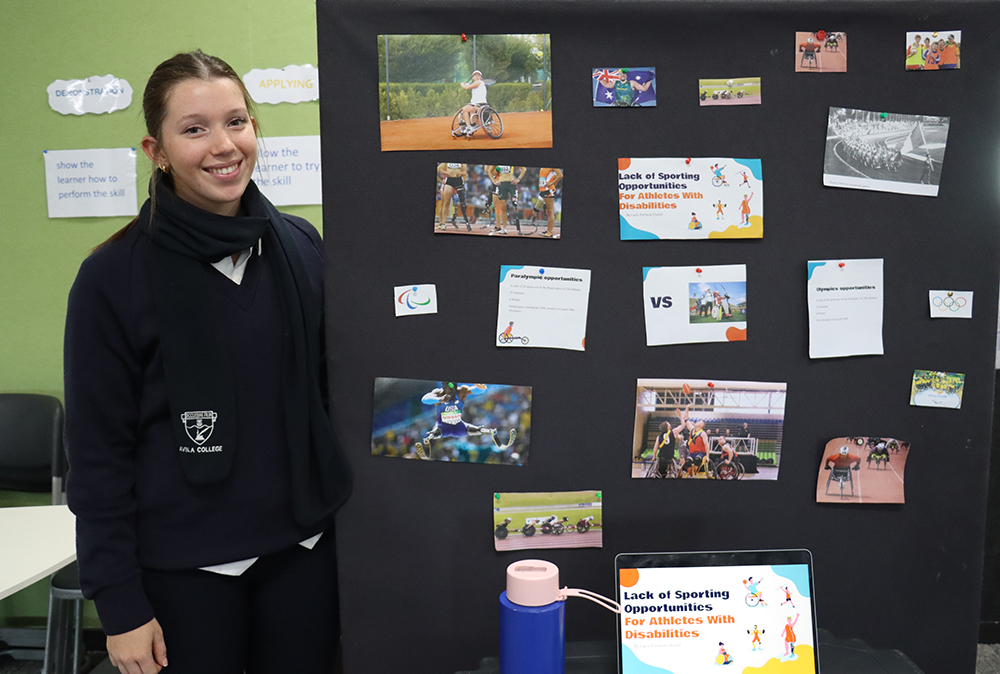
By investigating a range of contemporary issues associated with physical activity, sport and exercise, students explore factors that affect access, inclusion, participation and performance. Students then select one issue at the local, national or global level and analyse key concepts within the issue, including investigating, participating in and prescribing movement experiences that highlight the issue.
Students develop an understanding of the historical and current perspectives on the issue and consider the future implications on participation and performance.
Areas of Study
- How do physical activity, sport and exercise contribute to healthy lifestyles?
- What are the contemporary issues associated with physical activity and sport?
Unit Prerequisites
N/A
Study Design
Download the VCE Physical Education Study Design
Assessment
Assessment tasks for this unit are selected from the following:
- a written report analysing participation in at least 4 physical activities that demonstrates the integration of theoretical knowledge and practical application of how the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems work together.
- a practical laboratory report linking key knowledge and key skills to a practical activity or practical activities
- a case study analysis
- a data analysis
- an extended-response question that uses a visual planning tool such as a concept/mind map to synthesise information and develop a response
- a visual presentation such as an annotated poster, a concept/mind map, or a digital presentation (including physical simulation)
- an oral presentation such as a podcast or debate.
- a written plan or multimedia presentation designed to either increase physical activity levels and/or reduce sedentary behaviour for an individual or a selected group, based on reflections from participation in physical strategies/programs designed to promote physical activity and limit sedentary behaviour.
 View Physical Education Career Bullseye
View Physical Education Career Bullseye
Physical Education
Units 3+4


Overview
Unit 3 | Movement Skills and Energy for Physical Activity, Sport and Exercise
This unit introduces students to principles used to analyse human movement from a biophysical perspective. Students use a variety of tools and coaching techniques to analyse movement skills and apply biomechanical and skill-acquisition principles to improve and refine movement in physical activity, sport and exercise. They use practical activities to demonstrate how correctly applying these principles can lead to improved performance outcomes.
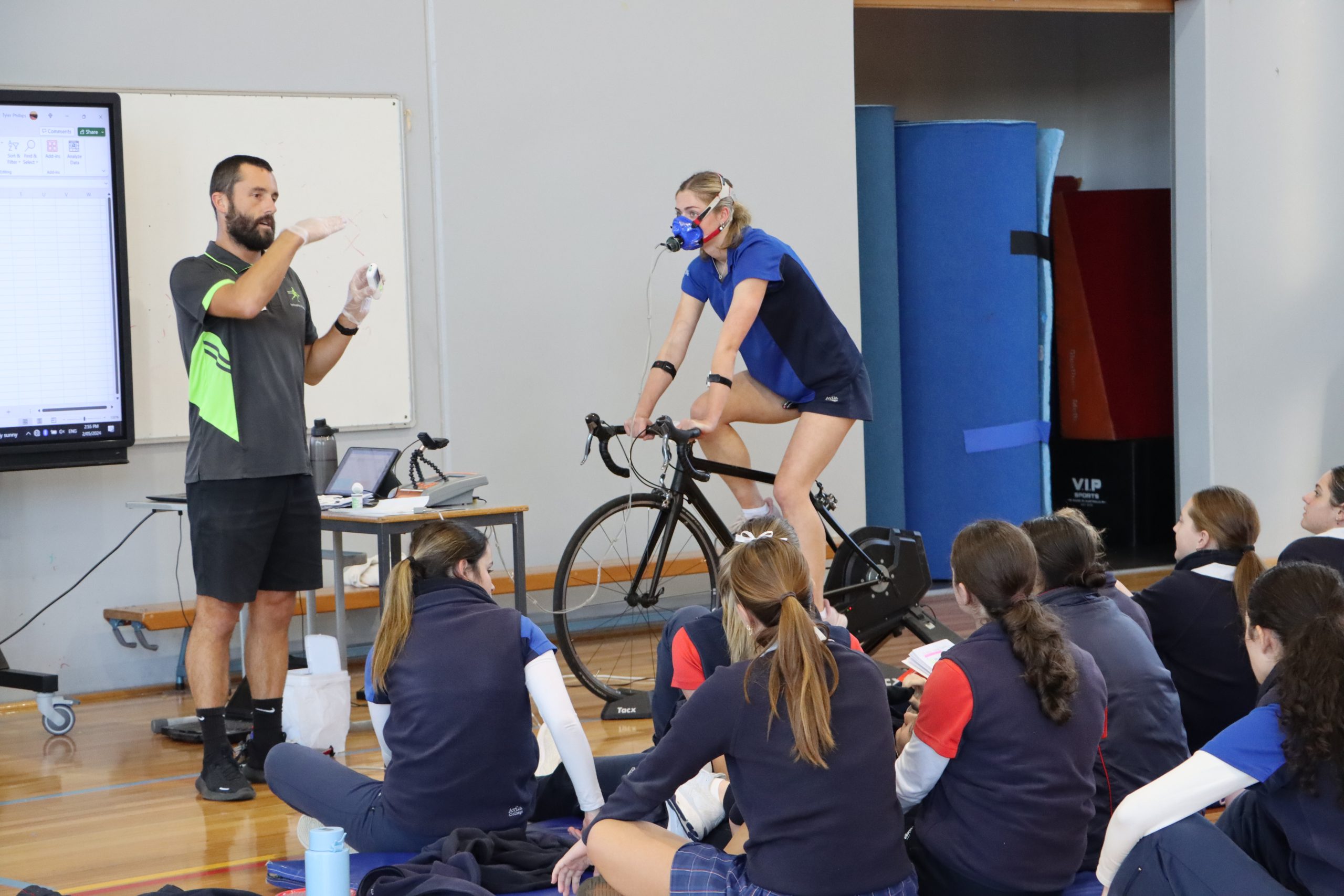
Students consider the cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems and the roles of each in supplying oxygen and energy to the working muscles. They investigate the characteristics and interplay of the 3 energy systems for performance during physical activity, sport and exercise. Students explore the causes of fatigue and consider different strategies used to postpone fatigue and promote recovery.
Areas of Study
- How are movement skills improved?
- How does the body produce energy?
Unit 4 | Training to Improve Performance
In this unit, students’ participation and involvement in physical activity will form the foundations of understanding how to improve performance from a physiological perspective. Students analyse movement skills and fitness requirements and apply relevant training principles and methods to improve performance at various levels (individual, club and elite).
Improvements in performance, in particular fitness, depend on the ability of the individual and/or coach to gain, apply and evaluate knowledge and understanding of training. Students assess fitness and use collected data to justify the selection of fitness tests based on the physiological requirements of an activity, including muscles used, energy systems and fitness components. Students then consider all physiological data, training principles and methods to design a training program. The effectiveness of programs is evaluated according to the needs of the individual and chronic adaptations to training.
Areas of Study
- What are the foundations of an effective training program?
- How is training implemented effectively to improve fitness?
- Integrated movement experiences
Unit Prerequisites
N/A
Study Design
Download the VCE Physical Education Study Design
Areas of Study
- What are the foundations of an effective training program?
- How is training implemented effectively to improve fitness?
- Integrated movement experiences
Assessment
Assessment tasks for this unit are selected from the following:
- Structured questions that draw on primary data that analyses a movement skill using biomechanical and skill-acquisition principles
- A laboratory report based on primary data collected during participation in a practical activity, which analyses the acute responses to exercise, energy system characteristics, energy system interplay, fatigue and recovery
- A written report analysing data from an activity analysis to determine the relevant physiological requirements in a selected activity including justification of the selection of appropriate tests to assess fitness.
- A case study that draws on experiences from participation in at least 5 training sessions to design a personalised 6-week training program
- A response in one or more of the following formats, which links chronic adaptations of the cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems to training methods and improved performance: a case study analysis, a data analysis, structured questions
- An extended-response question drawing on personal experiences from a chosen practical activity recorded in the reflective folio, that analyses the interrelationships between skill acquisition, biomechanics, energy production and training program theoretical knowledge for their impacts on participation and/or performance. An emphasis should be placed on using a suitable tool, such as a concept or mind map, to plan a response.
 View Physical Education Career Bullseye
View Physical Education Career Bullseye
Health and Human Development
Units 1+2

Overview
Unit 1 | Understanding Health and Wellbeing
In this unit, students explore health and wellbeing as a concept with varied and evolving perspectives and definitions. They come to understand that it occurs in many contexts and is subject to a wide range of interpretations, with different meanings for different people. As a foundation to their understanding of health, students investigate the World Health Organization’s (WHO) definition and other interpretations. They also explore the fundamental conditions required for health as stated by the WHO, which provide a social justice lens for exploring health inequities.
In this unit, students identify perspectives relating to health and wellbeing, and inquire into factors that influence health attitudes, beliefs and practices, including among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples. Students look at multiple dimensions of health and wellbeing, the complex interplay of influences on health outcomes and the indicators used to measure and evaluate health status. With a focus on youth, the unit equips students to consider their own health as individuals and as a cohort. They build health literacy by interpreting and using data in a research investigation into one youth health focus area, and by investigating the role of food.
Areas of Study
- Concepts of health
- Youth health and wellbeing
- Health and nutrition
Unit 2 | Managing health and development
In this unit, students investigate transitions in health and wellbeing, and human development, from lifespan and societal perspectives. They explore the changes and expectations that are integral to the progression from youth to adulthood. Students apply health literacy skills through an examination of adulthood as a time of increasing independence and responsibility, involving the establishment of long-term relationships, possible considerations of parenthood and management of health-related milestones and changes.
Students explore health literacy through an investigation of the Australian healthcare system from the perspective of youth and analyse health information. They investigate the challenges and opportunities presented by digital media and consider issues surrounding the use of health data and access to quality health care.
Areas of Study
- Developmental transitions
- Youth health literacy
Unit Prerequisites
N/A
VCE Study Design
Download the VCE Study Design for Health and Human Development
Assessment
Assessment tasks for this unit are selected from the following:
- a written report, such as a media analysis, a research inquiry, a blog or a case study analysis
- an extended response question analysing a range of data sources with an emphasis on annotating, synthesising and planning the response
- a visual presentation such as a graphic organiser, a concept/mind map, an annotated poster, a digital presentation
- an oral presentation, such as a debate or a podcast
- structured questions, including data analysis.
 View Health Career Bullseye
View Health Career Bullseye
Health and Human Development
Units 3+4

Overview
Unit 3 | Australia’s Health in a Globalised World
In this unit, students look at health and wellbeing, disease and illness as being multidimensional, dynamic and subject to different interpretations and contexts. They explore health and wellbeing as a global concept and take a broader approach to inquiry. Students consider the benefits of optimal health and wellbeing and its importance as an individual and a collective resource. They extend this to health as a universal right, analysing and evaluating variations in the health status of Australians.
Students focus on health promotion and improvements in population health over time. Through researching health improvements and evaluating successful programs, they explore various public health approaches and the interdependence of different models. While the emphasis is on the Australian health system, the progression of change in public health approaches should be seen within a global context.
Areas of Study
- Understanding health and wellbeing
- Promoting health in Australia
Unit 4 | Health and Human Development in a Global Context
In this unit, students examine health and human development in a global context. They use data to investigate health status and human development in different countries, exploring factors that contribute to health inequalities between and within countries, including the physical, social and economic conditions in which people live. Students build their understanding of health in a global context through examining changes in health status over time and studying the key concept of sustainability. They consider the health implications of increased globalisation and worldwide trends relating to climate change, digital technologies, world trade, tourism, conflict and the mass movement of people.
Students consider global action to improve health and human development, focusing on the United Nations’ (UN’s) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the priorities of the World Health Organization (WHO). They also investigate the role of non-government organisations and Australia’s overseas aid program. Students evaluate the effectiveness of health initiatives and programs in a global context and reflect on their own capacity to act.
Areas of Study
- Global health and human development
- Health and the Sustainable Development Goals
Unit Prerequisites
N/A
VCE Study Design
Download the VCE Study Design for Health and Human Development
Assessment
Assessment tasks for this unit are selected from the following:
- a written report, such as a media analysis, a research investigation, a blog post or a case study analysis
- an extended response question analysing a range of stimuli with an emphasis on annotating, synthesising and planning the response
- an oral presentation, such as a debate or a podcast
- a visual presentation, such as a concept map, an annotated poster, or a digital presentation
- structured questions, including data analysis or case study analysis.

